Quick Start
- Get boost/sml.hpp header
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/boost-ext/sml/master/include/boost/sml.hpp
- Include the header and define
smlnamespace alias
#include "boost/sml.hpp"
namespace sml = boost::sml;
- Compile with C++14 support
$CXX -std=c++14 ... | cl /std:c++14 ...
- To run tests
git clone https://github.com/boost-ext/sml && cd sml && make test
Dependencies
- No external dependencies are required (neither STL nor Boost)
Supported/Tested compilers
- Clang-3.4+
- GCC-5.2+
- MSVC-2015
- Known limitations
"src_state"_s + event<e> = "dst_state"_s // Error on MSVC-2015, Ok on GCC-5+, Clang-3.4+
state<class src_state> + event<e> = state<class dst_state> // Ok on all supported compilers
const auto guard1 = [] { return true; }
state<class a> + event<e> [ guard1 ] / [](const auto& event) {} // Error on MSVC-2015, Ok on GCC-5+, Clang-3.4+
const auto guard2 = [] -> bool { return true; }
state<class a> + event<e> [ guard2 ] / [](const auto& event) -> void {} // Ok on all supported compilers
Configuration
| Macro | Description |
|---|---|
BOOST_SML_VERSION |
Current version of [Boost].SML (ex. 1'0'0) |
Exception Safety
- [Boost].SML doesn't use exceptions internally and therefore might be compiled with
-fno-exceptions. - If guard throws an exception State Machine will stay in a current state.
- If action throws an exception State Machine will be in the new state
- Exceptions might be caught using transition table via
exceptionevent. See Error handling.
Thread Safety
- [Boost].SML is not thread safe by default.
- Thread Safety might be enabled by defining a thread_safe policy when creating a State Machine. Lock type has to be provided.
sml::sm<example, sml::thread_safe<std::recursive_mutex>> sm;
sm.process_event(event{}); // thread safe call
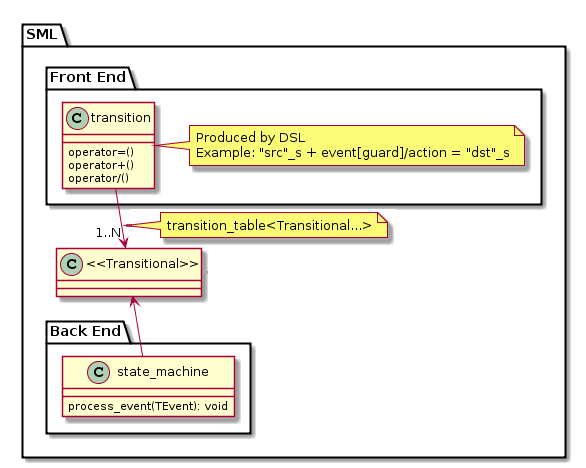
Design
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| [Front-End] | Transition Table Domain Specific Language |
| [Back-End] | State Machine implementation details |
Error messages
Not configurable
Not callable
Not transitional
Not dispatchable